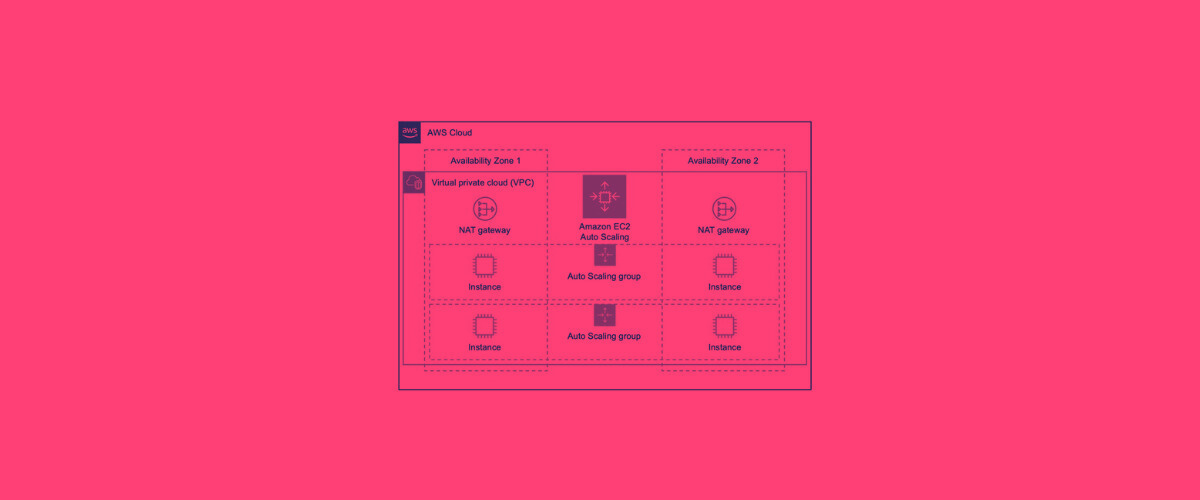
As enterprises embrace cloud-first architectures, building infrastructure that is secure, cost-efficient, and resilient is no longer optional, it is a strategic necessity. The AWS Well-Architected Framework (WAF) offers a structured methodology to assess and enhance cloud workloads across six foundational pillars. Whether modernizing legacy systems or fine-tuning cloud-native applications, aligning with WAF ensures the architecture upholds the highest standards of reliability, security, and governance.
📐 What Is the AWS Well-Architected Framework?
The AWS Well-Architected Framework is a set of guiding principles and best practices designed to help architects build secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient infrastructure for their applications. Itis not just a checklist, it is a mindset for continuous improvement.
🧱 The Six Pillars of WAF
| Pillar | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Operational Excellence | Monitoring, incident response, and automation for continuous improvement. |
| Security | Identity management, data protection, and threat detection. |
| Reliability | Fault tolerance, recovery planning, and workload availability. |
| Performance Efficiency | Resource selection, scalability, and evolving with technology. |
| Cost Optimization | Eliminating waste, right-sizing resources, and tracking spend. |
| Sustainability | Minimizing environmental impact and optimizing energy usage. |
🔐 Security: The Cornerstone of Enterprise Trust
For organizations in regulated sectors like utilities, security is not optional, it is foundational. The Security pillar emphasizes:
- Automated patching and vulnerability management.
- Centralized logging and GuardDuty integration.
- IAM least privilege and role-based access controls.
- Security Hub for continuous compliance monitoring.
⚙️ Operational Excellence: From Reactive to Proactive
This pillar encourages teams to:
- Define and document incident response playbooks.
- Implement automated remediation workflows.
- Use CloudWatch and AWS Config for real-time visibility.
- Continuously improve through post-incident analysis.
💸 Cost Optimization: Architecting for Efficiency
Cloud cost is not just about savings. It is about accountability. WAF recommends:
- Using AWS Cost Explorer and Budgets.
- Rightsizing EC2 instances and storage tiers.
- Leveraging Savings Plans and Spot Instances.
- Automating idle resource cleanup.
📊 Applying WAF in Enterprise Contexts
For solution architects, the framework becomes a blueprint for:
- Stakeholder alignment through structured reviews.
- Compliance mapping to ISO 27001, NIST, and CIS benchmarks.
- Risk mitigation via automated controls and audit trails.
- Documentation clarity for governance and reporting.
🧩 Scoping WAF Reviews for Enterprise Workloads
Ideally, WAF reviews should be conducted at the workload level where each workload represents a distinct application, service, or system with its own architectural footprint and business value.
Because workloads often vary in compliance obligations, performance expectations, and risk exposure, evaluating them individually ensures that each review is both contextually accurate and operationally relevant.
📆 Establishing a Continuous WAF Review Cadence
While some organizations schedule annual reviews for audit purposes, AWS recommends a more dynamic approach:
| Trigger | Frequency | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Major architectural change | As needed | E.g., migration, refactoring, new region deployment |
| Compliance or audit cycle | Annually or semi-annually | Aligns with ISO 27001, PDPA, or internal audit |
| Security incident or SLA breach | Immediately after | Ensures root cause analysis and remediation |
| Quarterly operational review | Every 3 months | Keeps workloads aligned with evolving best practices |
| CI/CD pipeline integration | Continuous | Automated checks during each deployment cycle |
🧭 Final Thoughts
The AWS Well-Architected Framework is not a one-time exercise. It is a continuous journey. By embedding its principles into the cloud strategy, you not only reduce risk and improve performance, but also build trust with stakeholders, regulators, and customers.
Next Up → How to Implement the AWS Well-Architected Framework